Worms in the human body are inherently non-viable parasites, they can only survive and multiply through the host (human or animal). Parasitic diseases in humans are caused either by the worms themselves or by their larvae. The disease spreads in an infectious way, the invasion of the helminths often goes unnoticed and gradually causes disruption in the body.
First of all, you should understand what helminths are. This is a general term for worms that parasitize the human body, the body of animals, or even plants. This explanation is also the answer to the question of what worms are. The terms "worm" and "helminth" are synonyms.
The most dangerous helminthic invasion is the long-term asymptomatic form, leading to diseases caused by malnutrition. Intestinal parasites live from the absorption of nutrients from the human body. Helminth invasion can be detected at an advanced stage after other symptoms of the presence of intestinal parasites have appeared.
Some intestinal parasite larvae can reach various tissues of the body. Inflammatory deposits form as the immune system recognizes the larvae as foreign organisms. Some immune system allergic reactions can occur as a result of the presence of helminths in humans.
When worms appear in a person, the symptoms and treatment for the invasion are closely related to eliminating the cause of the discomfort, that is, the parasite, and the signs of its presence also go away.
Routes of infection with parasites
There are many factors that make worms. Their appearance can be due to the following situations:
- One of the most common risk factors for helminthiasis is the influence of mass tourism;
- second is water and food contamination;
- Helminths can become infected after consuming meat products, sausages;
- poorly washed fruits and vegetables are the main source of parasite larvae;
- The transmission of worms from pets is often recorded.
Symptoms of parasitic diseases
A worm infestation can manifest itself differently depending on the type of parasite. The most common manifestations are as follows:

- Constipation - difficulty defecating from worms - is the result of a blockage in the flow of the bowel;
- Diarrhea - loose stools occurs when exposed to substances excreted by parasites that cause the loss of potassium and chloride;
- Flatulence and gas - parasites cause inflammation and gas in the small intestine;
- pain in muscles and joints - helminthiases are often characterized by the location of worms also in joint fluids and muscle tissue;
- allergy - parasites perforate the walls of the intestines, which allows undigested molecules to enter the bloodstream and cause an allergic reaction;
- Skin problems - with helminthiasis, skin problems such as acne, rash, and itching are common;
- anemia - parasites cling to the intestinal mucous membranes and "steal" nutrients, leading to anemia;
- granulomas - a tumor-like focus is formed that surrounds the eggs of parasites;
- Nervousness - worms produce toxins that irritate the central nervous system, which can cause mental symptoms;
- Sleep disorders - night terrors accompanies the helminth invasion for the following reasons: it is at this point that the worms leave the rectum, the activity of the liver increases, trying to get rid of the toxins they produce;
- chronic fatigue is one of the first signs of parasites in the body;
- oncological diseases.

Pinworms
Pinworms are one of the most common intestinal parasites in the human body. These worms are scientifically called Enterobiusvermicularis. They are spread all over the world. Although these worms are primarily characteristic of the child's body and are most common in children's groups, they are also found in the adult population.
Infection occurs when the parasite's larvae, which are somewhere around the infected person, are ingested. They are present on the skin, under the nails, in bedding, clothing, and dust. In the duodenum, the larvae develop into adult parasites, which then migrate to the large intestine.
Adult pinworms are about 1 cm long, thin, and resemble a white thread. They lay eggs in the perianal region. This is expressed in the most characteristic symptoms of the disease - discomfort and itching in the rectum area.
Complications of infection by parasites are chronic intestinal inflammation, in girls - secondary vaginal infection.
2/3 of people infected with intestinal parasites are not aware of helminthiasis because they often experience no symptoms other than fear, irritability and fatigue.
Vlasoslav
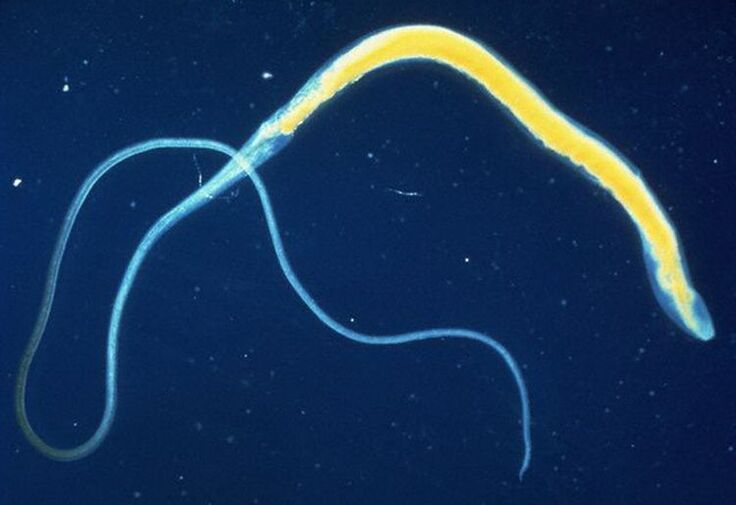
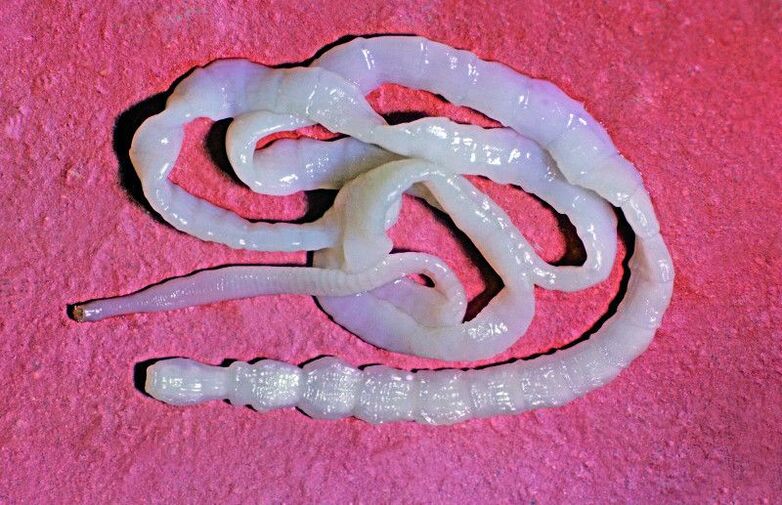
The second most common intestinal parasite is the whipworm Trichuristrichiura. Infections caused by this type of worm are usually asymptomatic, making it very difficult to accurately identify an infected person.
A fully grown whipworm is 3-5 cm long. Infestation occurs via the oral route - through the use of contaminated food or water, as well as through contaminated soil. The larvae of the parasite hatch in the small intestine, while the adult worms nest in the large intestine. The adult female lays eggs that hatch with feces and hatch in warm soil after 5 weeks of incubation.
In the worst case, the whipworm only causes abdominal pain, diarrhea or nausea. More serious complications of this infection occur only in tropical areas. In severe cases, chronic diarrhea or anemia can occur.
Nematodes
Human nematodes include 2 types of parasites - Ancylostomaduodenale and Necatoramericanus. Adult females are 10-13 mm (A. duodenale) or 9-11 mm (N. americanus), males 8-11 mm (A. duodenale) and 7-9 mm (N. americanus).
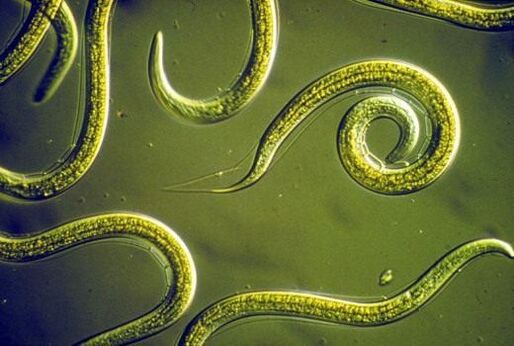
The eggs are excreted from the host's body in the feces. Under favorable conditions (moisture, warmth) the larvae hatch in the soil or in the faeces within 1–2 days, after 5–10 days they become infectious larvae. Under favorable natural conditions, they can survive for 3-4 weeks.
Contact with the human body occurs through the penetration of the parasite larvae through the skin. Through the bloodstream, they reach the heart and lungs, penetrate the alveoli, then travel from the bronchial tree to the throat and are swallowed by the person. The larvae enter the small intestine, where they remain for the time necessary for their development into adult worms.
Adult worms live in the small intestine, attach themselves to the intestinal wall and feed on the blood of their host, a human. Most of these parasites are eliminated from the body within 1–2 years, but the records of their parasitism in the body can reach dozens of years.
The larvae of A. duodenale worms that penetrate human skin are inactive (be it in the intestine or in the muscle). In addition, duodenal A. parasitic infection can also be transmitted orally. However, the N. americanus worm does require migration.
roundworm
Roundworms - Ascarislumbricoides - also belong to the intestinal parasites. An adult worm can grow up to 25 cm long. Helminths in a person of this type remain hidden for a long time. Your symptoms are mostly tiredness and coughing, which in most cases is due to other reasons.
When infected with helminthiasis, it is enough to use unwashed vegetables and fruits.
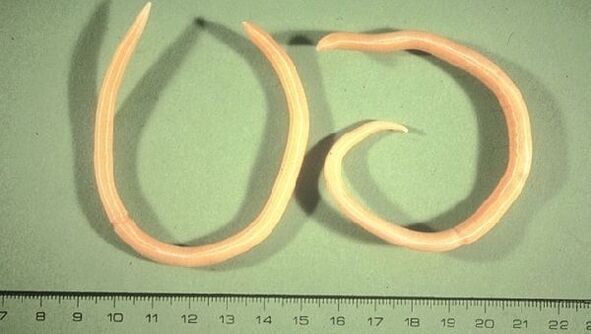
The larvae of these worms nest and hatch in the small intestine, penetrate the intestinal wall. Through blood and lymph flow, they get to the lungs and cause a cough. When coughing, greenish mucus is broken down, with which roundworms return to the intestines after swallowing. Ascaris eggs are excreted in the feces.
The most common source of infection between humans is infected human feces.
In severe cases, Ascaris can cause inflammatory processes in the body, most often pneumonia. In most cases, however, people infected with worms remain asymptomatic or the symptoms are so mild that neither the patient nor the treating doctor initially suspect an infection with intestinal parasites.
The disease caused by Ascaris is called ascariasis. The main route of infection is fecal-oral.
According to WHO estimates, the incidence of worms is around 1 billion people infected each year.
Helminths in adults, the symptoms and treatment of which depend on the localization of the worms, are characterized by a variety of clinical manifestations - from asymptomatic forms to severe, even fatal cases. Common symptoms include abdominal pain and aches and pains, diarrhea, rectal itching, or allergic manifestations. In the first - migratory - phase, the larvae of parasites can cause signs of inflammation of the lungs (Loeffler syndrome), the pancreas, the heart muscle, the liver and other organs.
Roundworms in the intestine are the cause of metabolic disorders and disorders of the nervous system.
Ascaris in the respiratory system
When worms migrate in the human body, they pass through the throat, where they colonize the lymph nodes around the main lymph chain (Waldeyer chain).
Where worm larvae may be present:
- Lymph and salivary glands;
- Throat;
- Larynx;
- the area along the ear canals that leads to the middle ear;
- all corridors that lead to the brain.
The side walls of the nasopharynx have openings that lead to the Eustachian tube that connects the throat to the middle ear. This allows the pressure in the ear to be equalized with the atmospheric pressure. In these ways, the larvae of the worms can reach the middle ear. As a result, hearing deteriorates, tinnitus appears, headache and Meniere's syndrome - dizziness, accompanied by moments of memory loss.
Pulmonary manifestations of Ascaris
With Ascaris lesions of the lungs, diseases of this organ and skin manifestations in the form of roughness and rash appear. These symptoms are accompanied by a slightly elevated temperature, but sometimes also by feverish states. The person suffers from a dry cough, asthmatic bronchitis, and hoarseness. If left untreated, pulmonary ascaris can develop into chronic problems with seasonal flare-ups and eventually cause severe bronchial asthma. The person becomes addicted to drugs and sometimes even retires with a disability pension.
Roundworms in other organs
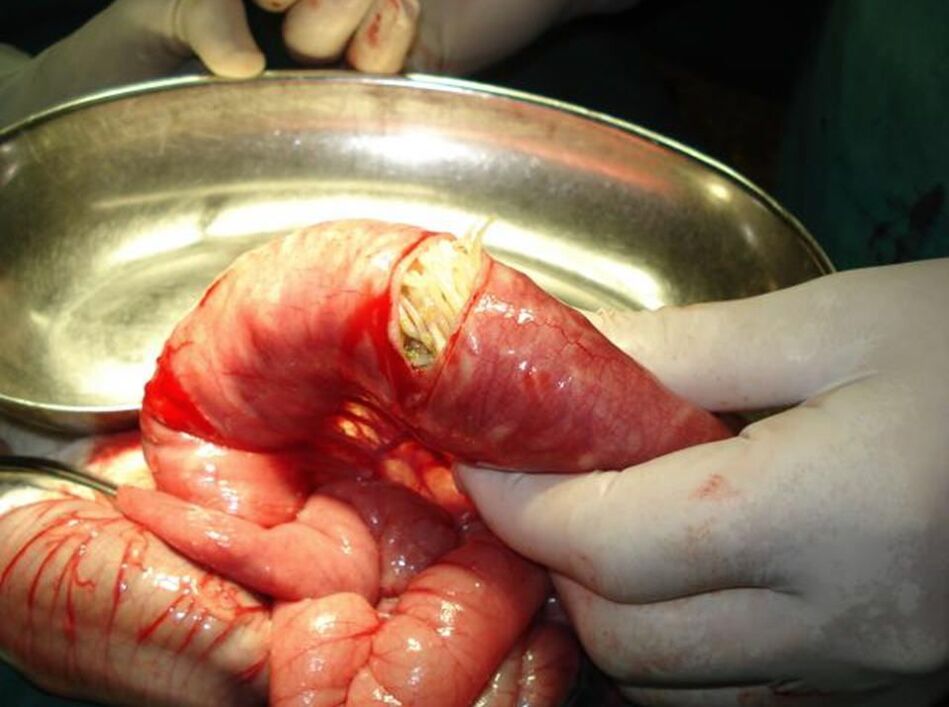
As the larvae of worms colonize other organs, they develop slight bleeding and signs of inflammation. They can penetrate the pancreas, biliary tract, and liver. In the small intestine, the larvae fuse into a "lump" and cause ileus. The parasite larvae live in the organs mentioned for life, feed on their metabolic products and damage them mechanically.
They can penetrate the pancreas, biliary tract, and liver. In the small intestine, the larvae fuse into a "lump" and cause ileus. The parasite larvae live in the organs mentioned for life, feed on their metabolic products and damage them mechanically.
In the presence of larvae in the liver and bile ducts, the liver is weakened and cannot naturally excrete toxic substances. As a result, they are excreted through the skin causing allergies, itchy rashes, subcutaneous swelling of "unknown" cause, and other manifestations in many variations, from dry eczema to purulent processes.
Ascaris in the brain
Symptoms of cerebral invasion vary depending on where the worm larvae are located. If they are in the meninges, there is a risk of meningoencephalitis with migraines. When the furrows are colonized, granulomas form in the gray crust.
Symptoms of brain cancer later appear: unconsciousness, epileptic seizures, convulsions. If the granuloma is near the optic or auditory nerve, deafness or visual impairment occurs.
Tapeworm
Chain - Taeniasaginata, Taeniasolium - is one of the oldest and most famous intestinal parasites. It can reach a record length - up to 9 m.

The two most common types of worms are cattle (Taeniasaginata) and pork tapeworm (Taeniasolium). Both types colonize the body after consuming raw or improperly cooked meat. The parasite's eggs are long and are deposited in the small intestine. Adult worms develop after 3 months. The end parts of the worm's body are filled with eggs, which are released one at a time and excreted with the feces. The larvae have the ability to enter the bloodstream through the intestinal lining and then migrate to the muscles and brain, where they settle.
Despite the severity of the disease, the tapeworm does not necessarily immediately cause symptoms of its presence, therefore it remains invisible for a long time. The chain in the muscles causes muscle pain, in the brain - epileptic seizures.
The parasite is detected by x-rays or computed tomography. An accurate diagnosis can only be made on the basis of these studies.
Parasite Treatment
Treatment methods for worms are many. This includes the popular use of anti-parasitic herbs as well as the most modern bioresonance therapy.
Antiparasitic Herbs
The rules for using anti-parasitic herbs are based on the location of worms in the body.

Reception half an hour before meals is advisable in the following cases:
- Parasites in the intestines and lower body;
- Secondary infection with worms of the genitourinary system.
Use with food: damage by parasites of the stomach, colon, liver and spleen.
Use after meals: Parasite infestation of the upper body, lungs, neck, head.
Recommendations for using anti-parasitic herbs:
- not recommended for pregnant women;
- Wormwood, one of the most widely used herbs for worms, shouldn't be used on stomach ulcers.
Chemical anti-parasitic drugs
The most effective are drugs that contain methyl carbamic acid. This active ingredient is intended to treat pinworms, whipworms, roundworms and tapeworms. When treating pinworms, the dosage is carried out according to the instructions. Treat other parasites with these drugs according to their age.
Adhering to the dosage is important to avoid cramps.
Treatment by applying therapeutic frequencies to a bioresonance device and using a plasma generator
These devices destroy pathogens in the body without any negative side effects. When using a bioresonance device, when using a plasma generator, electrical impulses penetrate the tissue - radio waves that cause the parasite membrane to vibrate. The result is a rupture of the membranes and consequently the destruction of parasites. A specific frequency is used for each type of microorganism.
In this treatment of worms, it is very important to observe the measures of the regime: the exclusion of alcohol consumption and subsequent detoxification. Dead worms must be removed from the body, otherwise they will be encapsulated and act like allergens.
Any parasites present will be eliminated by treatment with these methods. The therapy is carried out in 2 stages:
- Stage 1: removal of small parasites - 20 minutes for each microorganism;
- Stage 2 - Large Worm Removal - Frequency is applied first to destroy the eggs, then the larvae, and finally the adult worms.
Optimal therapy time:
- Protozoa: plasma - 5 minutes per frequency; Bioresonance - 20 minutes per frequency.
- Multicellular: plasma - 10 minutes per frequency; Bioresonance - 4 × 20 minutes with 1 frequency.
In addition to significantly shortening the intervention time, the use of a plasma generator has another major advantage - when it is used, up to 5 people can be present with animals at the same time. Its radius of action is up to 5 m.
diploma
Treating worms eliminates sugar, sweet baked goods, and potatoes - these foods create an ideal environment for helminths to survive.
When treating the child, it is recommended to give him roasted pumpkin seeds to chew - about 30 seeds three times a day. They should not be consumed with the main food.
Eating raw garlic in moderation also helps eradicate worms.
Getting rid of worms doesn't work without proper hygiene. Washing hands, frequent washing of bed linen, dishes is the basis of effective therapy.